|
The technical term “androgen” includes
true androgens
such as testosterone
and
dihydrotestosterone (DHT)
active on their
receptors,
but also precursors
of androgens such as the dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA),
dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate
(SDHEA), and A4-androstenedione,
as androgens’
metabolites among which androstanediol, androsterone and
their glucuronides derivatives (which are the principal
metabolites’ representatives).
ORIGINS OF ANDROGEN’S PRODUCTION IN WOMAN
Androgens’ are
produced daily:
-
In the ovaries
-
In the adrenals
·
In peripheral tissues
and constitute the total androgens’ production.
With ageing the daily androgen’s production varies in those
three pathways.
When the ovaries’ production of androgens decreases for one
or another reason (ageing, oophorectomy, menopause) the
total pool of androgens is diminished.
When the total daily production is sufficient they are no
symptoms of androgens’ deficiencies. This explains why women
don’t suffer from androgens’ deficiencies at the same age.
DAILY PRODUCTION OF ANDROGENS
During the normal
menstrual cycle
|
Testosterone and Estradiol productions in µg/day
during the normal menstrual cycle
|
| |
Estradiol
|
Testosterone
|
|
Proliferative phase
|
40 |
200 |
|
Secretory phase
|
200 |
200 |
Before menopause normal woman
produces each day 5
fold more testosterone than estradiol in the
proliferative phase and the same quantity in the secretory
phase (1)
|
Androgens’ precursors productions in µg/day
during the normal menstrual cycle
|
|
|
DHEA
|
DHEAS
|
Androstenedione
|
|
Proliferative phase
|
5.000 |
15.000 |
4.000 |
|
Secretory phase
|
5.000 |
15.000 |
4.000 |
Testosterone and dihydrotestosterone in woman
In woman plasma dihydrotestosterone represents almost 50 %
of testosterone levels:
|
Woman before menopause :
Plasmatic hormonal concentrations in ng /ml
|
|
Testosterone
|
0,57 ± 0,19
ng/ml
|
|
Dihydrotestosterone
(DHT) |
0,27 ± 0,06
ng/ml
|
Testosterone Dihydrotestosterone and mesterolone
MOLECULAR STRUCTURES
|
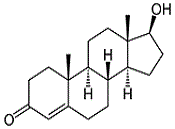
Testosterone
|
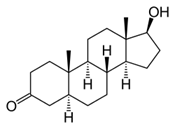
Dihydrotestosterone
|
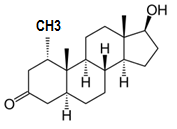
Mesterolone
|
Mesterolone has the structure of
testosterone with a methyl group on C1.
Depending from its
molecular structure Mesterolone
1) has properties similar to those of
testosterone (see appendix
chemical formula
2)
Depending from its
molecular structure Mesterolone has
properties similar to those of
dihydrotestosterone
|
